Windows 11 is out and updating on many machines, and in the process a lot of PC builders are tripped up by an odd system requirement: TPM 2.0. A TPM, or Trust Platform Module, is a dedicated processor that handles hardware-level encryption. It’s the device that allows you to use biometrics to log in to Windows and encrypt data on your device.
Still, it’s tough understanding what a TPM is, and more importantly, why you need one for Windows. We’re here to help you cut through the cryptographic weeds so you can get your PC up to spec to install Windows 11.
What is TPM?
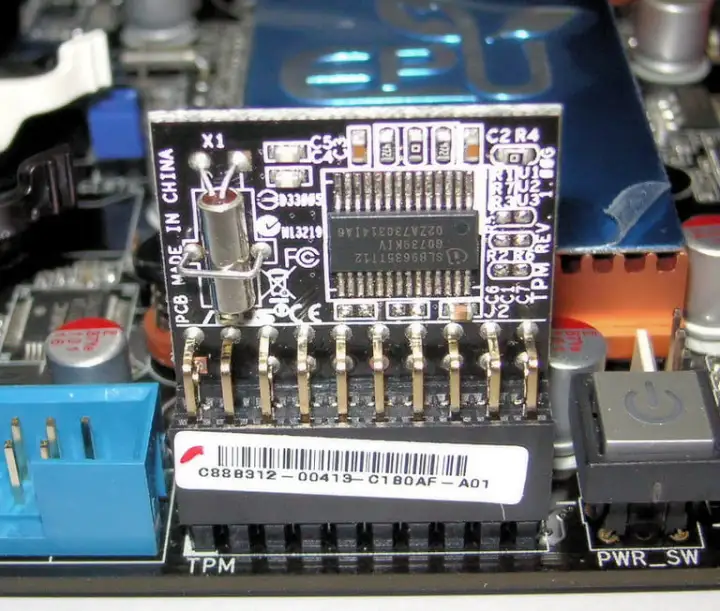
A TPM is a chip that lives on your computer’s motherboard. It’s a dedicated processor that handles encryption, holding part of the secret key you need to decrypt data on your device and access services. In the case of the upcoming Windows 11, the TPM can store things like your biometric data for Windows Hello and part of the encryption key for BitLocker.
That’s not the only purpose of a TPM, though. It can store any part of a secret you need for decryption, regardless if that’s a password, certificate, or encryption key. Furthermore, the TPM stores this information on actual hardware, not through software. That means software attacks can’t expose the secrets you have stored on the TPM.
A dedicated TPM further raises security thanks to a static Endorsement Key (EK) certificate. This certificate lives on the module and never changes, verifying that any component communicating with the TPM is, indeed, communicating with the TPM.
In short, a TPM helps you protect your most sensitive data. Because the device lives on your motherboard, it doesn’t need to communicate with any server or require further, offsite authentication. It’s a device that helps prove you are who you say you are, and that you’re accessing a computer you own.
Why you need TPM for Windows 11
It’s not hard understanding what a TPM does, but its application in Windows is a little messy. As mentioned, Windows 10 and Windows 11 use the TPM for BitLocker disk encryption and Windows Hello. The integration with Windows goes a lot deeper, though, which has caused some confusion with
Windows takes control of the TPM while your computer is booting. This is a good step for a couple of reasons. The first is that the TPM can verify the integrity of Windows before the operating system loads. That ensures you aren’t loading into an OS that has malicious code.
It also helps with antivirus software. Most malware is written to run on your OS, so something like adware executes after the operating system has loaded, even if you don’t see the program actively running on your desktop. Antivirus services can usually deal with this type of malware, but some struggle with rootkits.
A rootkit is a piece of malware that’s supposed to live on your computer undetected. Although some rootkits only attack a particular application, many start loading before your OS does. That opens up a world of possibilities to attackers, allowing them to infect the bootloader of your OS or even the kernel (the core of your OS).
TPM handles that. Windows automatically leverages the TPM during boot sequences, but other software, such as antivirus, can also leverage it to weed out rootkits before the OS loads.
Cyberattacks continue to rise, likely in response to the increasing amount of personal (and valuable) data that people store on their PCs and online. The TPM requirement on Windows 11 is the medicine before the candy. By getting PCs up to date with the latest hardware security, Microsoft can push forward with its security efforts rather than focus on getting more people on board.
Hardware TPM vs. firmware TPM

After the announcement of Windows 11, the price of dedicated TPM hardware has shot up on the secondhand market. Prices have dropped since, but it shows how much of a fuss this requirement caused. You don’t need to spend an extra $100 to run
This is mainly an issue for the DIY PC market, as Microsoft has required TPM on devices running Windows 10 for the past several years.
Off-the-shelf motherboards may not come with hardware TPM, but most boards from the last few years come with firmware TPM. Instead of a dedicated crypto-processor, this form of TPM uses firmware stored elsewhere on your motherboard for authentication. It then borrows your CPU’s horsepower to handle the cryptographic functions.
Hardware TPM is more secure, simply because it’s isolated from other components in your PC. If one component or area of your PC is compromised, the TPM can still function independently. Firmware TPM isn’t as isolated. It still performs the same function as hardware TPM, but its more prone to tampering since an attacker can, theoretically, more easily corrupt firmware over physical hardware.
Windows 11 doesn’t care about the type of TPM you’re using, so long as it adheres to the TPM 2.0 standard. If you built your own computer in the last few years, you can enable firmware TPM through your motherboard’s BIOS. If you bought a prebuilt machine or laptop, you’re fine to run



