Windows 11 might have a memory leak problem. As various Windows Insiders have pointed out, the Windows 11 File Explorer seems to hog memory even after it’s closed, slowly building a reserve of RAM that it’s not using. After installing Windows 11 to give the release version a shot, I had to see if the problem was still present.
It seems like it is. I was able to reproduce the issue several times, always falling around the same utilization mark. There’s a little more to the story, though. Windows 11 could have a memory leak problem, but it looks like Windows 10 does, too.
What even is a memory leak?
A memory leak is when a program takes up memory and doesn’t release it once you close the window. Essentially, it eats up the RAM it needs while open and fails to return that RAM to the pool once you close it. Memory leaks are fairly common, showing up everywhere from Google Chrome to AMD’s Catalyst Software at different points.
For Windows 11, the problem is focused on the File Explorer. In short, each time you open File Explorer and close it, you’ll slowly build a backlog of RAM that’s being used by the program, even while you’re not using it. This certainly looks like a memory leak, and it’s been an ongoing problem with preview builds of
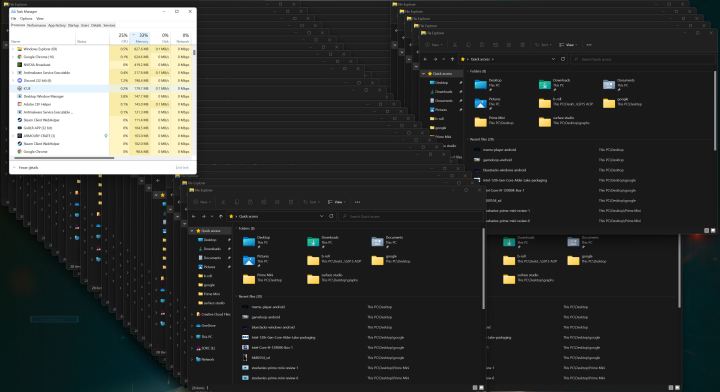
Following in the footsteps of PCGamer, I installed the latest build of Windows 11 on my gaming PC and started spamming File Explorer windows. I opened up Task Manager to monitor usage and opened just over 50 windows (until File Explorer was at the top of the list for memory utilization). After closing all of the windows, the utilization dropped, but not anywhere close to what File Explorer was consuming at idle.
At idle, File Explorer consumed about 80MB of memory, and after opening 50 windows, it jumped to 640MB. Even after closing the windows and waiting for a couple of hours, File Explorer was still eating up about 420MB of memory. I sanity-checked myself by opening and closing one window at a time and monitoring the usage, slowly watching as the utilization climbed in 3MB chunks each time.
I tried about a dozen times more, slowly watching as my utilization climb to over 1GB and stay there — all without a single File Explorer window open.
I’ll be the first to say that Task Manager is not the most reliable program for monitoring resource usage. I opened up Resource Monitor to double-check. After doing the process again, the amount of memory listed in Task Manager showed up in Resource Monitor under the Private tab. That means it’s memory being used by the task that can’t be shared with another program. So no, this isn’t a case of releasing memory when another program calls for it.
That was enough evidence for me, and I started writing up this post. That was until our esteemed computing editor Luke Larsen pointed something out: Does Windows 10 have the same problem?
Wait, Windows 10 has this problem too?

Yes, Windows 10 has a memory leak problem, too, and it has for years. A search of “Windows 10 memory leak” will produce dozens of reports from the last few years of memory leaks on Windows 10. Most, if not all, have been resolved by various updates over the past few years. I had to test that myself.
So, I booted up a separate Windows 10 machine — just to make sure it wasn’t a problem with my RAM modules themselves — and ran through the same process. I took an idle baseline, opened and closed 50 File Explorer windows, and hung out for 10 minutes. This is the same amount of time it took Windows 11 to reach 420MB of utilization, where it remained around for a couple of hours afterward.
It produced the same results, but not on the same scale. At idle, File Explorer in Windows 10 took up about 60MB of RAM, and with 50 windows open, it jumped to 307MB. After closing and waiting 10 minutes, it dropped back down to 95MB.
That’s an increase of 58% after opening and closing 50 windows on Windows 10, but a massive 425% increase on Windows 11. You can get around the issue by opening Task Manager and restarting the Windows Explorer task. But even then, I watched as the utilization ticked up on
I gave Windows 10 the same treatment by repeating the process about a dozen times. And after I had closed the final window, the utilization was still much higher than it should be. Over the course of an evening, though, Windows 10 graciously returned the utilized memory to the reserves. Windows 11 didn’t.
A bug, but not a big deal

There seems to be some problem with the Windows 11 File Explorer, and it looks a lot like a memory leak. The larger issue is unsuspecting users stumbling into a PC that feels much slower over time. Even opening up 50 File Explorer windows with 32GB of memory, my gaming PC slowed down a lot. On my XPS 13 with Windows 10, File Explorer crashed several times.
No one should reasonably open up 50 windows at once. That’s not the point here. That point is that, over time, you could clog your memory reserves with File Explorer windows that aren’t present, and the only way to clean the pipes is to restart the task in Task Manager or restart your computer entirely.
As I’ve said in the past, I’m waiting to upgrade to Windows 11 until these kinks are ironed out. After all, this issue was first reported two months ago, and the build of Windows 11 I installed today produced similar behavior. It could be a big memory leak, or it could be a small memory leak that’s also present on Windows 10, just blown up by File Explorer taking more memory on
Memory leaks happen with a lot of programs, and the worst thing you’ll need to do to resolve them is restart your computer. I don’t want to make this issue sound bigger than it is. That said, machines with 8GB or less of memory could start to feel sluggish quickly with this problem, and it seems Windows 11 amplifies the issue.